Essential Superfoods and Eating Tips
For brain and heart health, reduced stress, and protecting yourself from diseases, here are fifteen superfoods that deliver these benefits across all of those categories: fatty fish, blueberries, dark leafy greens, walnuts, dark chocolate, avocados, broccoli, sweet potatoes, pomegranates, green tea, beets, and turmeric.
Rather than eating all daily, experts recommend rotating 3-5 foods per day or splitting intake between breakfast and dinner for optimal absorption and sustainability.
Let’s get down to the details.
Brain-Boosters
Your brain requires specific nutrients to function at optimum performance.
-
-
- Omega-3 fatty acids are one of the main ingredients to pay attention to. Foods such as salmon are a good start. It contains the nutrient DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and is one of the three main types of omega-3s, which make up approximately 40% of the brain’s fatty acids. These are crucial for memory, learning, and cognitive performance.
- B vitamins support brain energy and help to create the chemical messengers that ‘talk’ to the other brain cells.
- Choline helps produce acetylcholine, essential for memory and learning.
- Antioxidants like vitamins E and C protect brain cells from oxidative stress, while flavonoids from berries and dark chocolate improve memory and protect against cognitive decline.
Top Brain Nutrients, Summary
-
-
-
-
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin E, C
- Choline
- Antioxidants
-
-
Heart-Healthy Essentials
The same omega-3 fatty acids that benefit your brain also support cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, lowering blood pressure, and improving cholesterol.
Fiber from plant sources helps lower cholesterol and support healthy blood sugar levels, while potassium regulates blood pressure and supports proper heart rhythm.
Stress-Fighting Nutrients
Magnesium is often called “nature’s relaxant” because it helps calm the nervous system and regulate cortisol levels. Omega-3 fatty acids significantly reduce stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline while supporting mood-regulating neurotransmitters. B vitamins are essential for stress resilience, as stress rapidly depletes these nutrients. Vitamin C acts as a natural stress buffer by supporting adrenal gland function.
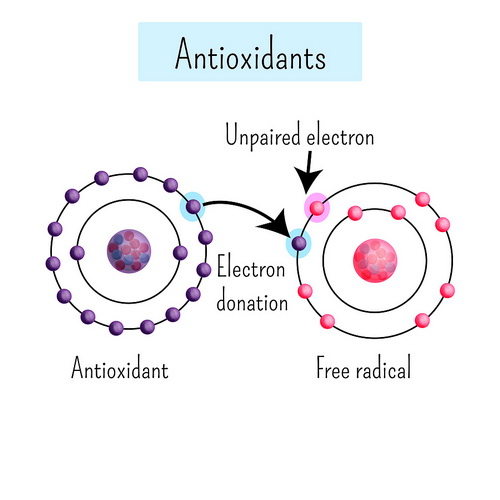
The Power of Antioxidants
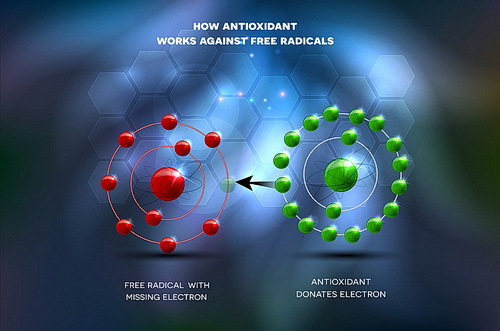
Antioxidants serve as your body’s defense system against cellular damage. Free radicals, unstable molecules that form from normal body processes and external factors like pollution, can cause a chain reaction of cellular damage.
Antioxidants neutralize these free radicals, preventing damage that can lead to heart disease, cancer, cognitive decline, and premature aging. Think of antioxidants as rust prevention for your cells.
Protein: The Body’s Building Block
Proteins provide the amino acids needed to build and maintain muscle, bone, skin, hair, and organs. Most enzymes and many hormones are proteins that regulate vital functions. Protein supports your immune system, maintains fluid balance, transports substances through your bloodstream, and is the most filling macronutrient, helping you feel satisfied longer and potentially supporting weight management.
The Superfood All-Stars

After analyzing these nutrients, these fifteen foods stand out as true superfoods that deliver comprehensive benefits across all these health categories:
| Food | Brain Health | Heart Health | Stress Relief | Antioxidants | Key Nutrients |
| Salmon | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA, DHA), Vitamin D, B vitamins, Selenium |
| Mackerel | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA, DHA), Vitamin B12, Selenium, CoQ10 |
| Sardines | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA, DHA), Calcium, Vitamin D, B vitamins |
| Walnuts | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), Vitamin E, Magnesium, Polyphenols |
| Blueberries | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Anthocyanins, Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Manganese, Flavonoids |
| Spinach | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Folate, Iron, Vitamin K, Lutein, Zeaxanthin, Magnesium |
| Kale | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Vitamin K, Vitamin C, Beta-carotene, Lutein, Calcium |
| Dark chocolate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Flavonoids, Magnesium, Iron, Theobromine, Phenylethylamine |
| Avocados | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Monounsaturated fats, Potassium, Folate, Vitamin K, Fiber |
| Broccoli | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Folate, Sulforaphane, Fiber |
| Sweet potatoes | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Beta-carotene, Vitamin A, Potassium, Fiber, Vitamin C |
| Pomegranates | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Punicalagins, Anthocyanins, Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Folate |
| Green tea | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | EGCG, L-theanine, Catechins, Caffeine, Polyphenols |
| Beets | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Nitrates, Betalains, Folate, Manganese, Fiber |
| Turmeric | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Curcumin, Manganese, Iron, Vitamin B6, Fiber |
For easier clarification, you can view our Superfood infographic.
The Practical Approach: Why Less Can Be More
While these superfoods offer incredible benefits, trying to eat all fifteen every single day isn’t practical or necessary. Attempting to do so could backfire for several reasons:
Overwhelming Your System: Even healthy foods contain calories, and consuming too many nutrient-dense foods at once can overwhelm your digestive system and lead to discomfort.
Practical Limitations: The cost, preparation time, and sheer volume of food would make this approach unsustainable for most people.
Diminishing Returns: Your body can only absorb and utilize so many nutrients at once. Spreading intake throughout the day and week is more effective than cramming everything into each day.
Individual Tolerance: Some people may have sensitivities to certain foods or may not digest large amounts of fiber or rich foods well.
Smart Strategies for Superfood Success
The Rotation Method
Instead of eating all fifteen foods daily, aim to include 3-5 different superfoods each day, rotating your choices throughout the week. For example:
-
-
- Monday: Salmon, spinach, blueberries
- Tuesday: Walnuts, kale, dark chocolate
- Wednesday: Avocado, broccoli, green tea
-
The Staples Strategy
Choose 5-7 foods from the list that you enjoy and can easily incorporate regularly, then rotate in others as available. You might have spinach and walnuts most days, salmon twice a week, and seasonal fruits when they’re fresh and affordable.
The Meal-Splitting Approach
Divide your superfood intake between breakfast and dinner. This strategy offers several advantages:
-
- Better nutrient absorption as your body processes nutrients more effectively when spread throughout the day
- Sustained energy from steady nutrient intake rather than overwhelming your system at once
- Practical portion sizes that fit comfortably into two meals
- Blood sugar stability from protein and healthy fats at both meals
For breakfast, consider a spinach and walnut omelet with berries, or a smoothie with kale, blueberries, and dark chocolate. For dinner, try salmon with roasted broccoli and beets, or a kale salad with pomegranate seeds.
Quality Over Quantity
Remember that consistency matters more than perfection. It’s better to regularly eat a few of these nutrient-dense foods than to stress about checking every box daily. Your body accumulates these benefits over time, so sustainable, enjoyable eating that supports your health long-term is the ultimate goal.
Maximizing Your Strategy
Timing Considerations
Pay attention to when you consume certain foods. Have green tea at breakfast rather than dinner for better sleep, consume heavier foods like fatty fish and nuts earlier in the day for energy, and opt for lighter vegetables and proteins in the evening.
The Synergy Effect
These foods work synergistically – their combined effects are often greater than the sum of their benefits.
The omega-3s in salmon work better when combined with the antioxidants in leafy greens, and the iron in spinach is better absorbed when paired with the vitamin C in broccoli.
The Bottom Line
Incorporating superfoods into your diet doesn’t have to be complicated or overwhelming. By understanding which nutrients support brain function, heart health, stress management, and antioxidant protection, you can make informed choices that support your overall wellness.
Focus on variety, consistency, and sustainability rather than perfection. Choose foods you enjoy, prepare them in ways that fit your lifestyle, and remember that small, consistent changes often lead to the most significant long-term benefits.
Your body is remarkably adaptable and resilient when given the right tools. By providing it with these nutrient-dense superfoods regularly – even if not all at once – you’re investing in your cognitive function, cardiovascular health, stress resilience, and overall vitality for years to come. Start with one or two superfoods that appeal to you, gradually expand your repertoire, and enjoy the journey toward better health through better nutrition.