We previously discussed the top foods are for brain health, but some supplements have been studied to be healthy for your brain as well. With all the advertising about this subject, let’s take a look at what ingredients are nutrients act as the real stimulants for your brain cells.
Hippocampus
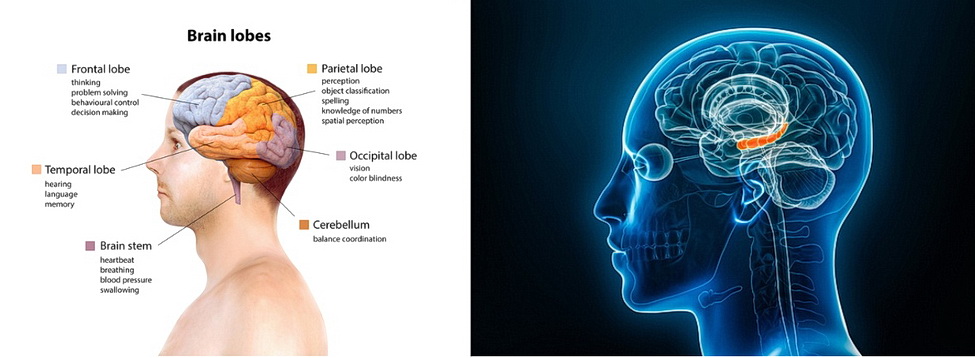
Before we delve into brain cells, it is important to note which part of the brain has the most influence on cognitive functionality: the hippocampus. Located in the medial temporal lobe, it is associated with learning and memory functions.
The Cells
While there isn’t a single type of cell responsible for memory, several cell types play crucial roles:
Neurons
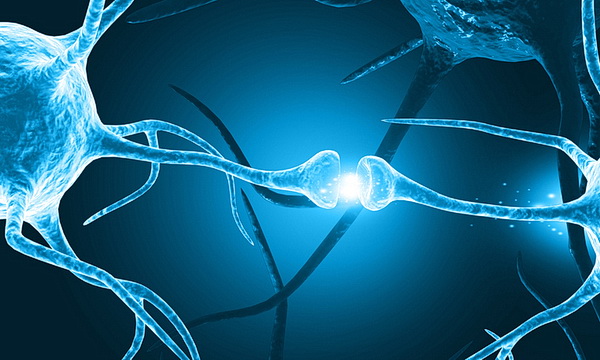
Neurons are the primary cells in the brain responsible for transmitting and processing information. Certain types of neurons, particularly those involved in long-term potentiation (LTP) and synaptic plasticity, are crucial in memory. These neurons form connections (synapses) with other neurons, and the strength and efficiency of these connections are believed to underlie memory formation.
Glial Cells
Glial cells, the unsung heroes of the brain, including astrocytes and microglia, are not just support staff for neurons. As recent research suggests, they also have active roles in synaptic transmission and plasticity, which are the building blocks of memory formation.
Neurotransmitters
Several neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin, modulate synaptic transmission. In layman’s terms, this means that they control the communication between neurons at the synapse, which is the gap between two nerve cells where neurotransmitters are released and received.
This is the fundamental process underlying memory formation.
Neurogenesis
Contrary to the long-held belief that neurogenesis, the birth of new neurons, is a one-time event in the brain’s development, recent evidence suggests it’s a lifelong process in certain brain regions, including the hippocampus. These fresh neurons are believed to contribute to specific memory processes, adding a fascinating layer to our understanding of memory formation.
Stimulating specific brain regions or cell types through transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or optogenetics can modulate neural activity and potentially enhance memory formation. However, the precise mechanisms underlying memory formation are still an active research area.
Cognitive Function Enhances
Now that we’ve grasped the functions of cells in the brain, let’s delve into some substances that bolster these cells, ensuring their vitality and health. While this compilation isn’t exhaustive, it serves as a starting point for identifying key components in brain-enhancing supplements, commonly referred to as nootropics.
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
DHA is food for your brain cells. It’s a healthy fat that keeps the cells strong and flexible, similar to how eating veggies helps your body remain healthy. When you have enough DHA in your diet, it supports the health of all kinds of brain cells, assisting them to communicate better and work more efficiently. This can lead to improved memory, learning, and overall brain function.
DHA is part of the omega-3 fatty acid family and consequently, it helps keep the cell receptors healthy. Cell receptors are located on the surface of cells or inside the cell. They serve as “sensors” that can recognize and bind to the neurotransmitters; in other words, they help enhance the singling process of the neurons. And as an FYI, you can also help your cell receptors by eating fish, especially salmon.
Choline
No, you don’t need to get it from a swimming pool, but you can get it in a supplement. Research has found that choline supplementation may have cognitive benefits, particularly in memory and attention. It is believed to enhance cognitive performance in adults and may reduce the risk of cognitive decline with aging.
Huperzine A
This is a natural compound derived from the Chinese club moss plant, Huperzia serrata. It works on neurotransmitters, specifically, it keeps acetylcholine alive and well by prohibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking it down. By inhibiting this enzyme, Huperzine A can increase the levels of acetylcholine; thus, it maintains neural transmission, which is important for memory, learning, and overall cognitive function.
Huperzine A has been studied as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. Some research suggests that it may improve memory and cognitive function in individuals with these conditions.
It is important to note that while Huperzine A shows promise as a cognitive enhancer, more research is needed to understand its effects and potential long-term benefits and risks fully. Like other nootropics, it should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
B Vitamins
B vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folic acid (B9), play a crucial role in brain function. They help the body convert food into energy for cells, including brain cells and are important for the production of neurotransmitters that regulate mood, memory, and focus.
Summary
While the field of nootropics continues to evolve, it is evident that certain ingredients hold promise in supporting memory, focus, and overall cognitive well-being. However, further research and regulation are imperative to ensure safety, efficacy, and ethical use for some of them.
Here we gave a summary of some of the components of the brain and some potential brain enhancing ingredients. As we navigate this exciting frontier further it is essential to approach brain enhancement with a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the possibilities and limitations of these ingredients in enhancing our cognitive abilities.









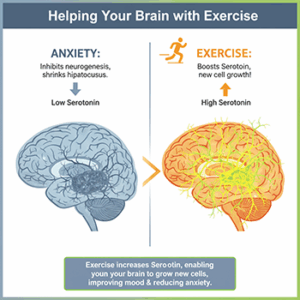
 June 27th is National PTSD awareness day. While there is still a general lack of understanding of
June 27th is National PTSD awareness day. While there is still a general lack of understanding of  Alzheimer’s disease is an aggressive neurological disorder that slowly breaks down brain cells and inhibits bodily function. The main problem materializes when a person starts to forget things as their brain cells gradually die.
Alzheimer’s disease is an aggressive neurological disorder that slowly breaks down brain cells and inhibits bodily function. The main problem materializes when a person starts to forget things as their brain cells gradually die.  Ah, the beauty of exercise! What can one say but only good things about this natural, physical full-body enhancement?
Ah, the beauty of exercise! What can one say but only good things about this natural, physical full-body enhancement?