https://www.freepik.com/pikisuperstar
What is COVID-19?
Coronavirus is part of a family of respiratory illnesses called SARS-CoV-2. It originated in China in 2019. Currently, it is commonly referred to as COVID-19, but some people may still refer to it as COVID-19.
When the virus first came out in late 2019, it was extremely destructive to the body’s immune system, especially to those that are immune deficient and the elderly, but since then, the symptoms from the new variants have subsided and those that have been vaccinated stand even less of a chance of getting very ill.
As of this writing, there have been over 6 million deaths worldwide and over 660 million cases.
The latest strain is the BA-5 variant, but cases of death or serious illness have subsided and those who have been vaccinated have stated they just feel like they have a cold.
How Is It Spread?
Covid is spread primarily through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. If there is someone nearby, that person can easily pick up the droplets and acquire the disease.
You can also catch the virus through infected hands or infected objects such as door knobs. You won’t acquire it by just touching an infected area, but if these objects are infected and you touch them and then you touch parts of your face, such as your nose, or any area where the virus can reach your mucus membranes, you can get infected.
That is why it is highly recommended to carry an antibacterial cleanser with you and to wash your hands as often as possible, especially after touching common objects such as entrance doors at retail stores.
Some people who have become infected may not exhibit symptoms, especially now in 2022, but others such as people aged 65 years and older and those with underlying medical conditions are still at a higher risk for severe consequences.
Are the Virus Cells Alive?
No virus is alive. Cells the other hand are very much alive. They are the building blocks of life.
What is the Difference Between Covid and the Flu?

They are both are respiratory illnesses, but they are caused by different viruses; in another word, their genetic coding varies enough to classify them differently. With that said, Covid is associated with the SARS-CoV-2 family and the flu is caused by the influenza virus family.
There are additional differences as well. Covid has been found to spread more easily than the flu. It is also known to be more severe. COVID-infected individuals can take a longer time for their symptoms to show and may they can be contagious for a longer period.
Can You Get COVID-19 if You Have Been Vaccinated?
Yes. Anyone, vaccinated or not can catch the disease, but if you are vaccinated, especially if you have received the booster shots, you are most likely not going to get it severely.
If you are vaccinated and do get COVID-19, you still need to quarantine since you can spread it to others.
What Does the Vaccine Do?
The coronavirus vaccines produce additional antibodies in the body. Antibodies act like a barrier between the virus and healthy cells. You might look at it as a wall that keeps the virus from attacking the healthy cells.
Is the Rapid Test as Good as a PCR Test?

No. The 15-minute rapid test is commonly referred to as the “home test” but it is used at medical facilities as well. Researchers state that these tests are only partially effective.
Why Do Some People Refuse to Take the Vaccine?
Some people are simply afraid to take the shot as they have heard stories about people who have gotten sick from it. Although this is true for some, they recover usually about 24 hours later, while many others have not felt any side effects at all. Other people have religious reasons and the last group is those that just believe that it is not necessary.
What Should I Do If I Acquire the Disease?

Drink lots of water. Make sure you are taking vitamins such as Vitamins C and D, as well as Zink, but most of all, sleep is extremely important because your body regenerates as you are sleeping.
You should start feeling better after about four days, but if you don’t see improvements by the 3rd or 4th day, don’t hesitate to call your doctor. They may prescribe you Paxlovid, which is a set of pills made by Pfizer that is known to accelerate the process of recovery.
If you are elderly or have an immune deficiency or another health ailment, let your doctor know and they most likely will prescribe Paxlovid to you immediately.
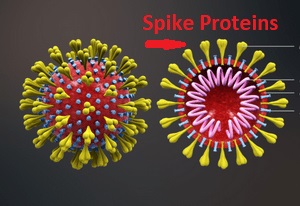
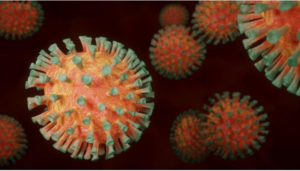
How Does the Virus Attack Human Cells?

It is all about the spikes that protrude out of the virus cells and are used to inject healthy cells which will mutate those cells and subsequently cause illness to the host.
Does Cold Weather Cause You to Get Covid More?
Yes, it can. According to theweathernetwork.com, “In the cold, the virus not only hangs in the air but also stays active longer“. Additionally, when winter comes, more people tend to stay inside where the chances of catching the virus intensify, especially if you are in close quarters with others.
How Can I Protect Myself from COVID-19?

You can work in many ways to prevent being infected with the virus.
Here are the main ones:
- Wash your hands with antibiotic liquid after touching anything outside of your home.
- Soap is better to use than antibiotic liquids if you have access to it.
- Stay at least six feet away from other people.
- Avoid places where there are large groups of people and if you just must go (e.g. supermarket, etc.) look for times when it is the least crowded.
- Wear a mask!
When Will This Pandemic Be Over?

As of the start of the new year, 2023, a new Omicron strain XBB.1.5 has materialized and according to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is very contagious; however, as with the previous variants, if you have been vaccinated and up to date with your boosters, your symptoms should be no more than a bad cold.
But if you are autoimmune or elderly, you still need to take extra precautions as with the other variants.
As far as when this will be over, the first sign will be when it changes from an epidemic to a pandemic. As of today, the symptoms have diminished greatly but the variants are still out there.
With that said, it is still recommended to take the necessary precautions. Wear a mask when near others, carry antibacterial cleansers with you, and wash your hands frequently!







 Around 2/3
Around 2/3