
Photo by alenkasm – yayimages.com
Even so, there are innumerable instances where women experience difficulty when they are expecting. Despite exercising due diligence, pregnancy complications may introduce various intricacies to the equation. These obstacles can affect the mother’s health and the well-being of the fetus. Such issues can make childbirth a high-risk procedure and be a concern for those involved.
So what are the potential predicaments that pregnant women may encounter? Let’s take a look.
Miscarriage
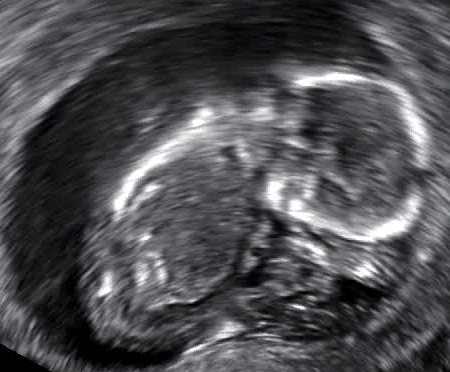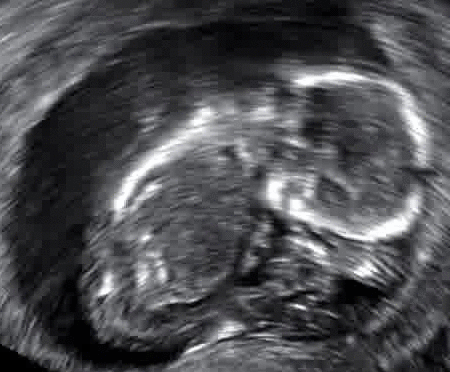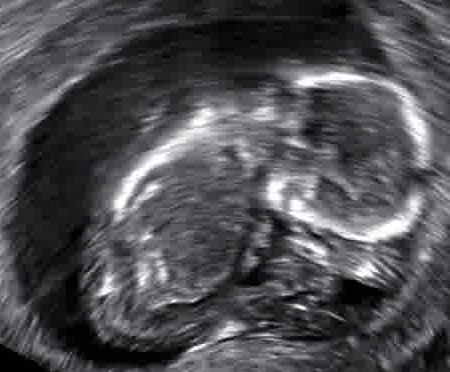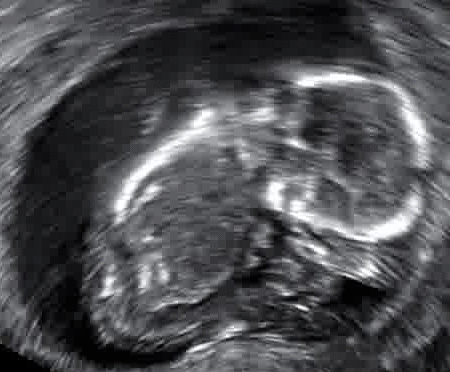
Furthermore, in terms of symptoms, the first indication of a miscarriage is that vaginal spotting or bleeding may appear. Regardless of the potential advent of a miscarriage, a pregnant female should consult a gynecologist at the first instance if there is bleeding. If the specialists suspect a miscarriage is underway, they may order an immediate ultrasound to gauge if the uterus is stable.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, a miscarriage is the most frequent cause of pregnancy loss. Research has shown that chemical pregnancies account for up to 75% of all miscarriages. This scenario transpires in the aftermath of implantation which gives rise to excessive bleeding when the woman experiences her period.
Causes of miscarriage include, but are not limited to hormonal problems and maternal health concerns. Also, a woman’s lifestyle and ill-conceived choices may be the reason for a miscarriage. For instance, if a woman who is expecting does not abandon her smoking habit, has a poor diet or does not kick drug use could lead to a miscarriage. Malnutrition and abundance of caffeine are other potential reasons. So are maternal age and maternal trauma.
Likewise, there is no definitive list of symptoms that a pregnant woman may exhibit. However, the most common red flags include different degrees of back pain, which may be considerably worse than menstrual cramping. Weight loss is another potential signal and so are regular contractions, which may occur every five minutes or so.
Preeclampsia
 This is a condition that transpires exclusively when a woman is expecting and entails extraordinarily high blood pressure and protein in their urine or liver. Also, they may have kidney abnormalities in the second trimester.
This is a condition that transpires exclusively when a woman is expecting and entails extraordinarily high blood pressure and protein in their urine or liver. Also, they may have kidney abnormalities in the second trimester.
Preeclampsia is a severe ailment that affects roughly 5% of all pregnant women. Typically, most females who are expecting a child develop moderate signs as their due date approaches. However, with adequate care and conservative measures, both the mother and her newborn child do not suffer any consequences.
If not diagnosed properly and left unchecked, preeclampsia can cause deterioration of the woman and baby’s health quickly. It may incite organ issue and potentially life-threatening scenarios as well. This may cause an early delivery or a caesarian section, a medical procedure where surgical equipment is used to deliver a child.
Moreover, females who are in line to become mothers for the first time are most susceptible to contracting preeclampsia. Those with a track record of suffering from preeclampsia or gestational hypertension may also be prone to the affliction.
In addition, pregnant women who are carrying more than one child or those who are aged 40 and above may also face complications. The same rules apply to females with high blood pressure and those who are obese also.
For the mother, the possible impact of preeclampsia includes liver or renal failure and probable cardiovascular concerns at some point in the future. The potential damage is far greater for the unborn child. They may suffer from diminished oxygen and nutrition. This transpires when preeclampsia restricts the placenta from obtaining ample blood. This may result in the child being born with significantly lower weight.
Gestational Diabetes
In the United States, between 2 and 10 percent of expectant mothers contract gestational diabetes. Although the numbers may sound promising, this disease must not be underestimated, given that its severity may increase. Pregnant women are frequently tested in a glucose screening to observe if they are not victims of gestational diabetes.
In cases where the screening has a negative result, pregnant women are monitored by professionals. With the proper care, a majority of women are able to maintain their blood sugar levels with the right diet and exercise (there is a specific exercise regimen that can be adhered to during pregnancy). This allows them to deliver a healthy child eventually.
Mothers who suffer from gestational diabetes are also at greater risk of developing Type 2 diabetes in the future as well. Warning signs of gestational diabetes are the presence of sugar in urine. Obviously, it is not apparent to the naked eye but a test at the doctor’s office can determine its presence. Excessive thirst, considerable exhaustion and the feeling of nausea are other symptoms of gestational diabetes.
Placenta Previa
Another case of pregnancy-related issues is called placenta previa. The placenta lies lower than usual in the uterus which is how it covers part of the cervix. The placenta severs from the uterine wall while the cervix starts to dilate during labor.
Symptoms of placenta previa vary on a case by case basis but the most frequent signal is pain-free bleeding during the third trimester of pregnancy. Additionally, premature contractions, the child’s irregular position in the womb are also signs of placenta previa.
