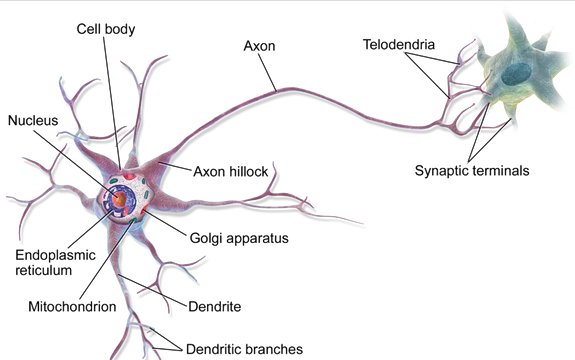
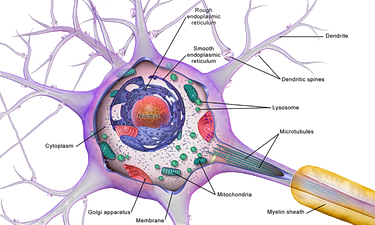
We have previously discussed the hundreds of trillions of cells, AKA neurons that exist in our brains. Just think about that for a second (or two). Now let’s see what holds all these nerve cells together!
What is the Brain Made of?
There are so many additional details to this piece of ugly gray matter that we haven’t spoken about yet, so now let’s dive into it.
By now, you should have a pretty good idea of what the neurons do, but what causes these nerve cells to react? Well, our sensors (sight, smell, hearing, touch and taste) have a lot to do with this.
When we sense something, our brain amasses the messages in a manner that has meaning to us; in other words, the nerve cells get to work in order to make us understand what just happened. If you touch something that is hot, say grab a coffee cup from freshly made coffee, that instinct of touch is translated into ‘neuron language’, where millions, perhaps billions of nerve cells get together in our brain to tell us that this item is hot. Of course, this happens instantly to us. Thousands of times faster than it took you to read this paragraph.
The Components of the Brain
So now that we can identify how the brain translates information, what are the different parts of the brain and how do they work?
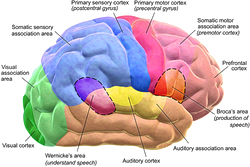
There are three parts. The cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
The Cerebrum
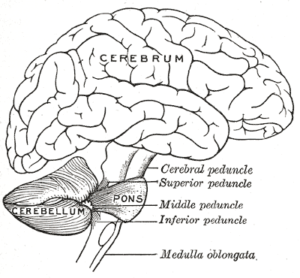
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Its function is remembering, problem-solving, thinking and feeling, and movement. The cerebrum is located in the lower back area of your brain.
There are two parts of the cerebrum called the right and left hemispheres, sometimes referred to as the right or left side of the brain. Interestingly enough, each side of the cerebrum controls the other side of the body, so if you have a stroke that comes from the left side, it will be the right side (namely your arms and legs) that will be affected.
The left cerebrum controls speech, comprehension, and math. A more generic way to label the left side of the cerebrum is that it focuses on logic or problem-solving. The left hemisphere is the dominant side for about 92% of the population, which is why so many people are right-handed.
For all of you Star Trek fans, ever wonder how Mr. Spock’s brain is assembled? He is of course a Vulcun whose species focuses specifically on logic, so is his left cerebrum more abundant (and the right side less abundant) proportionally? Or maybe he doesn’t have a right hemisphere at all? After all, he didn’t seem to be that great in music.
The right hemisphere controls creativity, art, and artistic and musical skills. Does that mean legends such as Leonardo da Vinci, Auguste Rodin, Irving Berlin, Michael Jackson, and Frank Sinatra had larger right hemispheres or that they just used that part of the brain more often?
Of course, when it comes to scientists, we’d like to deduce that Albert Einstein used his left hemisphere most often, but it is not as simple as that.
In an excerpt from Discover Magazine,
“Those who would explore Einstein’s brain are well aware they’re treading potentially controversial ground. Nevertheless, they believe they’re on to something. In 1985, neuroscientist Marian Diamond of the University of California, Berkeley, reported the Einstein brain had extra cells called glia. These cells support the “thinking” neurons in the left parietal lobe, an area above and behind the left ear involved in spatial relations and mathematics. She speculated that this “might reflect the enhanced use of this tissue in the expression of his unusual conceptual powers.” Seven years later, a researcher in Osaka, Japan, suggested a link between that higher glia-to-neurons ratio and Einstein’s purported dyslexia.”
Cerebellum
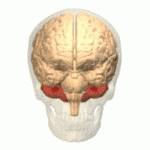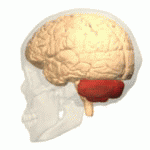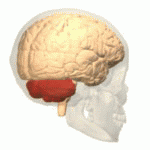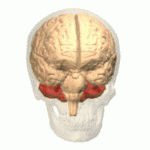
The cerebellum resides in the rear of the brain. Its functions involve coordinating voluntary movements such as motor skills, maintaining posture, equilibrium, and balance.
If the cerebellum is not performing correctly (e.g. brain injury, poorly developed, stroke, born with a defect) can result in numerous issues; such as asynergia, which is a motor coordination illness, dysmetria, makes it difficult to use your hands (e.g. trying to pick up a cup of coffee) and Parkinson’s Disease, which is a neurodegenerative disorder and involves tremors in the hands as well as compromised functionality in other parts of the body.
Brain Stem
Appropriately named because it connects to the spinal cord and resides in front of the cerebellum.
There are three major parts to this part of the organ:
Midbrain
The midbrain processes visual and auditory information.
Pons
This is the largest part of the brain stem. It’s located below the midbrain. It’s a group of nerves that help connect different parts of the brain. The pons also contains the start of some of the cranial nerves. These nerves are involved in facial movements and transmitting sensory information.
Situated beneath the midbrain, it is the largest part of the brain stem. It’s a gathering of nerves that interface with other parts of the brain. The pons is also part of a segment of the cranial nerves. These nerves are engaged with facial developments and sensory data.
Medulla Oblongata
Resides in the lower part of the brain. It acts as the control center for the function of the heart and lungs. It helps regulate many important functions, including breathing, sneezing, and swallowing.
This is where the heart and lungs are controlled and as such, it controls breathing and other heart/lung functions.
Conclusion:
This brief but rather definitive article gives some insight into how are brain functions and how these functions correspond to other parts of our body, so the next time you think, walk, talk or catch a baseball, consider how your brain made this happen and never take these motor skills for granted since there are some folks who are not as fortunate those with parts of the brain that do function well.
Here are some websites for neurological disorders. We hope you will consider donating!
Brain Diseases
Autism and Neurodevelopment
Parkinson’s Disease
Lou Gehrig’s Disease












 Many people underestimate the significance of foods that uplift the mood. A good demeanor is not just a fleeting mental phenomenon. By keeping your mood good, you can mitigate the effects of chronic stress. Mood also helps alleviate the symptoms of depression and anxiety. In short, how your mood fares affect your mental health and consequently dictates the quality of your life.
Many people underestimate the significance of foods that uplift the mood. A good demeanor is not just a fleeting mental phenomenon. By keeping your mood good, you can mitigate the effects of chronic stress. Mood also helps alleviate the symptoms of depression and anxiety. In short, how your mood fares affect your mental health and consequently dictates the quality of your life. 
 For many years,
For many years, 

 June 27th is National PTSD awareness day. While there is still a general lack of understanding of
June 27th is National PTSD awareness day. While there is still a general lack of understanding of 