Organic Compounds to Proteins
Organic compounds are the foundation of proteins, but do you know what they are? Unless you can remember your high school biology or you work in this field, chances are you don’t remember.
So how about we refresh our education on what these entities are and how they are related to viruses, especially, the SARS-CoV-2 (Covid) family of viruses?
Let’s start with the prerequisites. What organic compounds and amino acids are and then we’ll delve into proteins. We will keep our discussion simple so that you can get a clear understanding of it all.
Organic Compounds?
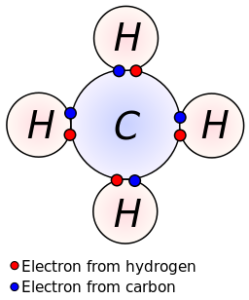
Quite simply, these are molecules where one or more of their atoms are linked to atoms of other elements. This can occur when atoms have less than eight electrons in their outer shell, which is known as the valence shell.
Atoms with ‘missing’ electrons in this shell will look to find how they can make up the difference, and this is done by combining its shell with electrons of other atoms so that it can balance into the required eight electrons in its valence shell. When this sharing process occurs, the molecules are known as covalent bonds.
What Makes Amino Acids?
An amino acid, AKA “amino group”, more popularly known as the building blocks of proteins, is an organic compound that shares atoms with specific elements.
These covalent bonds contain the atoms of hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The common atom that shares its elements with these elements is the carbon atom.
Amino Acids for Human Needs
Let’s talk about amino acids and why they’re so important for us! You might not know this, but our bodies actually need 20 different amino acids to stay healthy. But the catch? Not all of them are essential.
Out of those 20, there are nine that we really can’t live without. These are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Pretty cool, right? The thing is, our bodies can’t make these nine on their own, so we’ve got to get them from the food we eat. You’ve probably seen ads pushing protein supplements or protein-packed snacks. But honestly, you can find these essential amino acids in good old meat, eggs, and poultry.
What are Proteins?
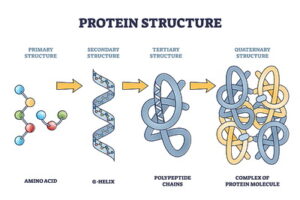
Now, onto proteins! So, what exactly are they? Well, proteins are basically long chains made up of hundreds, sometimes thousands, of amino acids linked together. They play a huge role in our body, especially in our cells, helping to keep our tissues and organs in tip-top shape.
Each amino acid is connected by something called a peptide, which is a fancy way of saying they’re linked together. And the cool part? There are tons of different proteins out there, each one doing its own job to keep us healthy. So, next time you think about what to eat, remember those amino acids and proteins are working hard to keep you feeling your best!
Proteins are essential to the body and help maintain the following that is most important for your health.
-
-
- Replenishment
Like a turnstile, proteins come and go. On a typical day, depending on the amount of energy you utilize, your body reduces a certain amount of proteins, so those proteins need to be replenished. If, after a while, those proteins are not replenished, your body can become weaker and prone to infections, as well as muscle and bone deficiencies. This is common in pregnancy and when you become ill. - Balances Fluids
- Transports and Stores Nutrients
- Bolsters Immune Health
- Replenishment
-
If you are not sure if you are getting enough proteins, here are some signs.
What Foods are Good in Protein?

Our body does not work alone when it comes to proteins. We need the right food to help replenish our health. According to WebMD, the following are highly recommended food sources for protein:
-
-
- Fish and particularly salmon, is not just good for protein health but is healthy in many other ways.
- Other seafood. Lobster lovers rejoice!
- Skinless, white-meat poultry
- Lean beef (tenderloin or sirloin)
- Skim or low-fat milk
- Skim or low-fat yogurt
- Fat-free or low-fat cheese
- Eggs
- Lean pork (tenderloin)
- Beans
-
Summary
Atoms contain electrons that reside around the nucleus. Covalent bonds are atoms that attach by sharing the same electrons in their outer shell.
Those that share electrons from a carbon atom are amino acids. There are 20 different kinds, with nine being essential for our health. Amino acids are molecules that link together in a chain to form proteins.
Some proteins require external intake (food) as your body doesn’t produce enough of them on its own.
Now let’s move on to What are Cells and What Do They Do?
