Overview
The human body is constantly facing threats from several external influences, such as pollution, viruses, and unhealthy diets, and free radicals are the major culprit. To fight off these cell killers, antioxidants are critical.
We discussed free radicals previously and how to fight them with antioxidants. Now, we will take a closer look at the role of radical cell fighters and how they help to maintain a healthy body. But before we get into the details, let’s review what free radicals are.
Free Radicals and the Role of Antioxidants

The human body constantly forms free radicals due to environmental factors, such as exposure to radiation, UV rays, tobacco smoke, and other forms of air and water pollution. However, free radicals are also a by-product of several processes that take place inside the human body. It might come as a surprise that free radicals may also be produced in the body due to exercise.
Moreover, free radicals are required for specific processes taking place in the body. For example, when the immune system gets charged up to fight any external invaders, such as a virus, it requires free radicals to damage the external intruder, such as a bacteria or virus. In all, free radicals are not always harmful.
What is the Problem With Free Radicals?
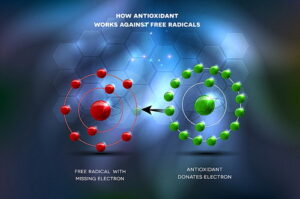
The concerning aspect of free radicals is that they do not have a complete set of electrons, so they look to steal their required electrons from other atoms, consequently damaging atoms and molecules in the process. To counter the effects of free radicals, the human body needs antioxidants.
Antioxidants work by donating their electrons to the free radical cells, so they don’t have to borrow electrons from the healthy molecules in the body. Moreover, antioxidants also facilitate the repair process of the cells that have donated their electrons to the free radicals. So antioxidants are an essential part of countering the free radicals in your body.
As the free radicals travel their path of cell destruction, they are met with antioxidant defenses to keep these free radicals in check, but then when the free radicals outnumber antioxidants we have a big problem. This can lead to a condition that is known as oxidative stress. Constant oxidative stress can damage your cells, including your DNA and other healthy molecules in your body.
As a result, prolonged oxidative stress can significantly increase the risk of several health conditions, including premature aging, cognitive decline, arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
Causes of Oxidative Stress

Certain lifestyle and environmental factors that can increase the risk of oxidative stress include:
-
-
- Exposure to radiation, cigarette smoke, and environmental pollution
- Excessive intake of alcohol, sugar, and polyunsaturated fats
- Excessive intake of micronutrients, including iron, magnesium, copper, or zinc
- Exposure to viruses, bacteria, and fungi
- Intense and constant workout sessions that can damage tissues
- An unhealthy diet that lacks antioxidants.
-
While the human body naturally produces some antioxidants, including glutathione and lipoic acid, they are not always enough to counter the free radicals produced by environmental factors.
Exploring the Environmental Factors

As mentioned, unhealthy dieting, alcohol consumption, and cigarette smoking can increase free radicals in the body, but it doesn’t stop there.
One example is the train derailment in New Palestine, Ohio, which had thousands of gallons of vinyl chloride stored in some of the cars on this 150-car train.
To prevent this toxic chemical from being exposed to the environment, authorities agreed to burn it, but that action has caused controversy in itself as questions arose about its chemical makeup being potentially still active.
Regardless of the manner in which the vinyl chloride was released into the air, citizens of New Palestine are concerned that this chemical will cause harm to them. Technically speaking, there could be an increase in oxidative stress for the citizens who live in the area, and in the case of vinyl chloride, it can cause drowsiness and nausea.
Similar concerns for other chemicals that were on the train are Butyl acrylate, which can cause eye irritation, and Isobutylene, which can cause dizziness and headaches.
Although the above is a unique case of potential exposure to toxic chemicals, pollution, in general, is always out there in one form or another (e.g., vehicle gas exhausts, generating electric energy), and that’s why there is an increasing emphasis on consuming foods that are rich in antioxidants.
What Foods are High in Antioxidants?

Below are the nutrients with antioxidant activity and the foods that can provide you with significant antioxidants. With that, note that the darker the fruit or vegetable, the more antioxidants they will have!
Phenolic Compounds
These plant compounds are found in apples, red wine, onions, grapes, peanuts, tea, cocoa, and all types of berries.
Vitamin C
Vegetables such as bell peppers, broccoli, cauliflower, brussels sprouts, kale, and cabbage are rich sources of vitamin C. Fruits, including grapefruit, honeydew, mango, kiwi, lemon, orange, and papaya, also contain a significant amount of vitamin C.
Vitamin E
Seeds and nuts, including almonds, sunflower seeds, and peanuts, contain a sufficient amount of vitamin E. Certain vegetables such as avocado, chard, leafy greens, and red peppers are also rich in vitamin E.
Selenium
A potent antioxidant is readily found in nuts, fish, beef, poultry, and whole grains.
CAROTENOIDS (Beta-carotene and Lycopene)
Carotenoids can be found in carrots, apricots, beet, asparagus, broccoli, bell peppers, kale, and cantaloupe. Fruits such as mangos, oranges, peaches, and grapefruits are also loaded with carotenoids.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants – What the Hype is All About?

Researchers started giving attention to antioxidants in the 1990s as they became more aware of the role of free radicals in coronary heart diseases. Around the same time, scientists also established a relationship between free radicals in the body and diseases, such as loss of vision, cancer, and several other chronic health conditions.
Given the results of several other similar studies, the media, and the food and supplement industries began to create hype about the benefits of “antioxidants.” It became a marketing buzzword for green teas, berries, and several other foods available on the store shelves. Moreover, the supplement industry also promoted the disease-fighting properties of antioxidants. The general public, unaware of the reality, got attracted to the antioxidant-rich breakfast cereals, energy drinks, and supplements.
However, that’s not how you can get the real benefits of antioxidants. So far, there is inconclusive evidence that the use of supplements and other processed food that claims to be “rich in antioxidants” provides real health benefits or not.
Indeed, antioxidants offer several health benefits, but you can only enjoy them if you consume antioxidants in their natural state. So instead of adding packaged and processed foods or supplements that claim to contain antioxidants, it is best to rely on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains that are loaded with natural plant compounds.
These naturally available antioxidants serve as great warriors to fight off free radicals and facilitate the natural repair process in the human body. Moreover, to get the maximum benefits of antioxidants, it is best to use them with other nutrients, plant compounds, and even with other antioxidants that your body requires.
Final Words
Oxidative stress caused by an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants can contribute to several chronic health conditions, including arthritis, cognitive impairment, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. But then it does not always mean the use of substances with antioxidant properties can fix the problem. It is especially true if these antioxidants do not come from a natural source. The studies provide evidence that naturally occurring antioxidants found in plants and vegetables can substantially impact diseases. However, there is inconclusive research on the benefits you can enjoy using supplements and other artificial sources of antioxidants that come in the form of processed foods.
So make sure you add a lot of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to your diet. At the same time, you need to limit your exposure to UV rays, radiation, and environmental pollution. Together, these two factors will reduce the risk of oxidative stress, which in turn will slow down the aging process while offering protection against several chronic diseases.
